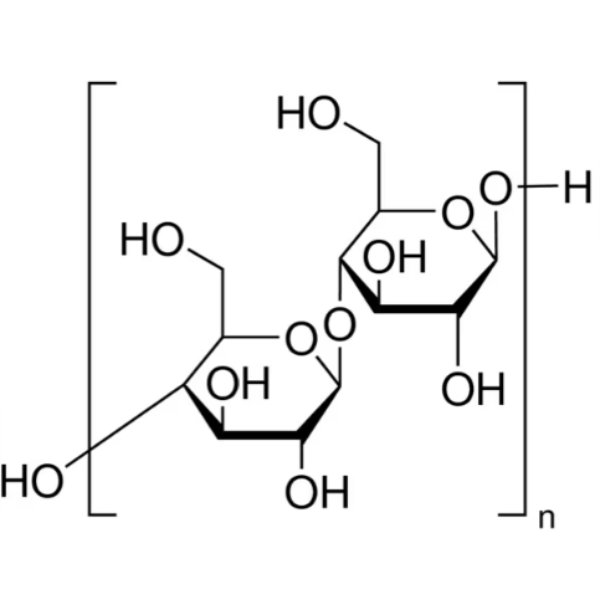
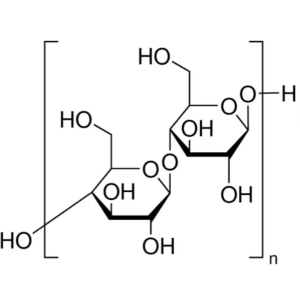
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) CAS 9004-34-6 Assay 97.0~102.0%
Shanghai Ruifu Chemical Co., Ltd. is the leading manufacturer of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) (CAS: 9004-34-6) with high quality. Ruifu Chemical can provide worldwide delivery, competitive price, excellent service, small and bulk quantities available. Purchase Microcrystalline Cellulose, Please contact: alvin@ruifuchem.com
| Chemical Name | Microcrystalline Cellulose |
| Synonyms | MCC; Cellulose Microcrystalline; Cellulose; Cellulose Powder; α-Cellulose |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Capacity 6500 Tons per Year |
| CAS Number | 9004-34-6 |
| Molecular Formula | (C6H10O5)n |
| Molecular Weight | 162.06 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 76.0~78.0℃ |
| Flash Point | 164℃ |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 (20℃) |
| Refractive Index n20/D | 1.504 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with Strong Oxidizing Agents |
| Storage Temp. | Store at Room Temperature, Keep Cool and Dry |
| COA & MSDS | Available |
| Origin | China |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Items | Inspection Standards | Results |
| Appearance | White or Off-White Powder | Complies |
| Solubility | Insoluble in Water, Ethanol, Acetone, or Toluene | Complies |
| Particle Size Distribution (+60Mesh) | 0-10% | Complies |
| Particle Size Distribution(+200mesh) | 40-100% | Complies |
| Water Soluble Substances | ≤0.25% | 0.015% |
| Ether-Soluble Substances | ≤0.05% | <0.05% |
| pH Value | 5.0~7.5 | 5.3 |
| Chloride (Cl) | ≤0.03% | <0.03% |
| Starch | Should Not Show Blue | Complies |
| Loss on Drying | ≤7.0% | 3.4% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.10% | <0.10% |
| Heavy Metals (Pb) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤2ppm | <2ppm |
| Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose | 10.0~20.0% | Complies |
| Microbial Limits | ||
| Total Aerobic Microbial Count | ≤1000 cfu/g | <10 cfu/g |
| Total Molds and Yeasts | ≤100 cfu/g | <10 cfu/g |
| Escherichia Coli | Not Detected /10g | Complies |
| Salmonella | Not Detected /10g | Complies |
| Assay | 97.0~102.0% | 98.0% |
| Infrared Spectrum | Conforms to Structure | Complies |
| Conclusion | The product has been tested & complies with the specifications | |
Package: Bottle, 25kg/kraft bag, 25kg/fiber drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse away from incompatible substances. Avoid exposure to excessive heat. Protect from light and moisture.
Shipping: Deliver to worldwide by air, by FedEx / DHL Express. Provide fast and reliable delivery.
Microcrystalline Cellulose
Cellulose [9004-34-6].
DEFINITION
Microcrystalline Cellulose is purified, partially depolymerized cellulose prepared by treating alpha cellulose, obtained as a pulp from fibrous plant material, with mineral acids.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Procedure
Iodinated zinc chloride solution: Dissolve 20 g of zinc chloride and 6.5 g of potassium iodide in 10.5 mL of water. Add 0.5 g of iodine, and shake for 15 min.
Sample: 10 mg
Analysis: Place the Sample on a watch glass, and disperse in 2 mL of Iodinated zinc chloride solution.
Acceptance criteria: The substance takes on a violet-blue color.
• B. Procedure
Sample: 1.3 g of Microcrystalline Cellulose, accurately weighed to 0.1 mg
Analysis: Transfer the Sample to a 125-mL conical flask. Add 25.0 mL of water and 25.0 mL of 1.0 M cupriethylenediamine hydroxide solution. Immediately purge the solution with nitrogen, insert the stopper, and shake on a wrist-action shaker, or other suitable mechanical shaker, until completely dissolved. Transfer an appropriate volume of the Sample solution to a calibrated number 150 Cannon-Fenske, or equivalent, viscometer. Allow the solution to equilibrate at 25 ± 0.1 for NLT 5 min. Time the flow between the two marks on the viscometer, and record the flow time, t1, in s.
Calculate the kinematic viscosity, (KV)1, of the Microcrystalline Cellulose taken:
Result= t1 × k1
t1= flow time (s)
k1= viscometer constant (see Viscosity 911)
Obtain the flow time, t2, for 0.5 M cupriethylenediamine hydroxide solutions using a number 100 Cannon-Fenske, or equivalent, viscometer.
Calculate the kinematic viscosity, (KV)2, of the solvent:
Result= t2 × k2
t2= flow time for 0.5 M cupriethylenediamine hydroxide solutions (s)
k2= viscometer constant
Determine the relative viscosity, rel, of the Microcrystalline Cellulose specimen taken:
Result= (KV)1/(KV)2
(KV)1= kinematic viscosity of the Microcrystalline Cellulose taken
(KV)2=kinematic viscosity of the solvent
Determine the intrinsic viscosity, []c, by interpolation, using the Intrinsic Viscosity Table in the Reference Tables section.
Calculate the degree of polymerization, P:
Result= (95) × [η]c/WS × [(100 %LOD)/100]
[η]c= intrinsic viscosity
WS= weight of the Microcrystalline Cellulose taken (g)
%LOD=value obtained from the test for Loss on Drying
Acceptance criteria: The degree of polymerization is not greater than 350.
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition 281: NMT 0.1%
• Heavy Metals, Method II 231: NMT 10 ppm
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests 61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms 62: The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 1000 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and for the absence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species.
• Conductivity
Sample: 5 g
Analysis: Shake the Sample with 40 mL of water for 20 min, and centrifuge. Retain the supernatant for use in the pH test. Using an appropriate conductivity meter that has been standardized with a potassium chloride conductivity calibration standard having a conductivity of 100 µS/cm, measure the conductivity of the supernatant after a stable reading is obtained, and measure the conductivity of the water used to prepare the test specimen.
Acceptance criteria: The conductivity of the supernatant does not exceed the conductivity of the water by more than 75 µS/cm.
• pH 791: 5.0–7.5 in the supernatant obtained in the Conductivity test
• Loss on Drying 731: Dry a sample at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 7.0% of its weight, or some other lower percentage, or is within a percentage range, as specified in the labeling.
• Bulk Density
Analysis: Use a volumeter that has been fitted with a 10-mesh screen. The volumeter is freestanding of the brass or stainless steel cup, which is calibrated to a capacity of 25.0 ± 0.05 mL and has an inside diameter of 30.0 ± 2.0 mm. Weigh the empty cup, position it under the chute, and slowly pour the powder from a height of 5.1 cm (2 in) above the funnel through the volumeter, at a rate suitable to prevent clogging, until the cup overflows. [Note-If excessive clogging of the screen occurs, remove the screen.] Level the excess powder, and weigh the filled cup. Calculate the bulk density by dividing the weight of the powder in the cup by the volume of the cup.
Acceptance criteria: The bulk density is within the labeled specification.
• Particle Size Distribution
[Note-In cases where there are no functionality-related concerns regarding the particle size distribution of the article, this test may be omitted.]
Where the labeling states the particle size distribution, determine the particle size distribution as directed in Particle Size Distribution Estimation by Analytical Sieving 786, or by a suitable validated procedure.
• Water-Soluble Substances
Sample: 5.0 g
Analysis: Shake the Sample with 80 mL of water for 10 min, and pass with the aid of a vacuum through filter paper (Whatman No. 42 or equivalent) into a vacuum flask. Transfer the filtrate to a tared beaker, evaporate to dryness without charring, dry at 105 for 1 h, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
Acceptance criteria: The difference between the weight of the residue and the weight obtained from a blank determination does not exceed 12.5 mg (0.25%).
• Ether-Soluble Substances
Sample: 10.0 g
Analysis: Place the Sample in a chromatographic column having an internal diameter of about 20 mm, and pass 50 mL of peroxide-free ether through the column. Evaporate the eluate to dryness in a previously dried and tared evaporating dish with the aid of a current of air in a fume hood. After all the ether has evaporated, dry the residue at 105 for 30 min, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
Acceptance criteria: The difference between the weight of the residue and the weight obtained from a blank determination does not exceed 5.0 mg (0.05%).
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers.
• Labeling: The labeling indicates the nominal loss on drying, bulk density, and degree of polymerization values. Degree of polymerization compliance is determined using Identification test B. Where the particle size distribution is stated in the labeling, proceed as directed in the test for Particle Size Distribution. The labeling indicates with which technique the particle size distribution was determined if a technique other than analytical sieving was used; and the labeling indicates the d10, d50, and d90 values and the range for each.
How to Purchase? Please contact Dr. Alvin Huang: sales@ruifuchem.com or alvin@ruifuchem.com
15 Years Experience? We have more than 15 years of experience in the manufacture and export of a wide range of high quality pharmaceutical intermediates or fine chemicals.
Main Markets? Sell to domestic market, North America, Europe, India, Korea, Japanese, Australia, etc.
Advantages? Superior quality, affordable price, professional services and technical support, fast delivery.
Quality Assurance? Strict quality control system. Professional equipment for analysis include NMR, LC-MS, GC, HPLC, ICP-MS, UV, IR, OR, K.F, ROI, LOD, MP, Clarity, Solubility, Microbial limit test, etc.
Samples? Most products provide free samples for quality evaluation, shipping cost should be paid by customers.
Factory Audit? Factory audit welcome. Please make an appointment in advance.
MOQ? No MOQ. Small order is acceptable.
Delivery Time? If within stock, three days delivery guaranteed.
Transportation? By Express (FedEx, DHL), by Air, by Sea.
Documents? After sales service: COA, MOA, ROS, MSDS, etc. can be provided.
Custom Synthesis? Can provide custom synthesis services to best fit your research needs.
Payment Terms? Proforma invoice will be sent first after confirmation of order, enclosed our bank information. Payment by T/T (Telex Transfer), PayPal, Western Union, etc.
Hazard Symbols Xi - Irritant
Risk Codes 37 - Irritating to the respiratory system
Safety Description 24/25 - Avoid contact with skin and eyes.
WGK Germany 3
RTECS FJ5950200
FLUKA BRAND F CODES 3
TSCA Yes
HS Code 39129090
Toxicity LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 2000 mg/kg
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) (CAS: 9004-34-6) is a purified, partially depolymerized cellulose that occurs as a white, odorless, tasteless, crystalline powder composed of porous particles. It is commercially available in different particle sizes and moisture grades that have different properties and applications.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is mainly used as non-caloric food additives, pharmaceutical excipients and dispersants, thin layer chromatography and column chromatography packing, colorants for dyes and pigments, reinforcing fillers for thermosetting resins and thermosetting laminates, coatings, emulsifiers, can also be used in the water-based paint and ceramic industries.
High purity cellulose powders for partition chromatography.
Cellulose is a thickener and an emulsifier. Cellulose (microcrystalline) is used as an emulsifier in cosmetic creams.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is widely used in food as anti-caking agent, stabilizer, absurbent, binding agent, edible fiber etc.
Suitable for textile, clothing, brewing, food, paper and other industries.
Microcrystalline Cellulose can be used as anticaking agent, emulsifier, dispersant, and binder. my country's "Hygienic Standards for the Use of Food Additives" (GB2760-2011) stipulates that it can be used for non-dairy powder and cream, with a maximum usage amount of 20g/kg; for ice cream, 40g/kg; high-fiber foods and bread, 20g/kg. Other reference for use: Use in ice cream can improve the overall emulsification effect, prevent the formation of ice slag, and improve the taste. Combined with carboxymethyl cellulose can increase the suspension of cocoa powder in milk beverages...
Microcrystalline Cellulose has the advantages of low density, high modulus, renewable, degradable and wide sources. It can be used as a reinforcing agent to improve the properties of composites.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is an important functional food base in the food industry - dietary cellulose, an ideal health food additive; used in the coating industry Its thixotropic and thickening properties can be used as a thickener and emulsifier for water-based paints; it is a kind of filler, thickening and emulsification in cosmetics, and has good emulsifying ability for oily substances; Used as a thickening and filler in the production of artificial leather, the artificial leather surface is smooth and uniform in thickness. It can be seen that the use of microcrystalline cellulose is very extensive, and the demand for this product in China will continue to increase.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents including bromine pentafluoride, sodium nitrate, fluorine, perchlorates, perchloric acid, sodium chlorate, magnesium perchlorate, F2, zinc permanganate, sodium nitrite, sodium nitrate, sodium peroxide. Nitration with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids produces Cellulose microcrystalline nitrates (celluloid pyroxylin, soluble pyroxyline, guncotton) which are flammable or explosive.
Cellulose is inert and is classified as a nuisance dust. It has little, if any, adverse effect on the lung, and there are no reports of organic disease or toxic effect. The health effects attributed to wood, cotton, flax, jute, and hemp are not attributable to their cellulose content but rather to the presence of other substances. Cellulose fibers were found in the blood and urine of human volunteers fed dyed cellulose; there were no ill effects.
Microcrystalline Cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is used to produce thixotropic gels suitable as suspending vehicles in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. The sodium carboxymethylcellulose aids dispersion and serves as a protective colloid. Concentrations of less than 1% solids produce fluid dispersions, while concentrations of more than 1.2% solids produce thixotropic gels. When properly dispersed, it imparts emulsion stability, opacity and suspension in a variety of products, and is used in nasal sprays, topical sprays and lotions, oral suspensions, emulsions, creams and gels.
A nuisance dust. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is widely used in oral pharmaceutical formulations and food products and is generally regarded as a relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material. Microcrystalline cellulose is not absorbed systemically following oral administration and thus has little toxic potential. Consumption of large quantities of cellulose may have a laxative effect, although this is unlikely to be a problem when cellulose is used as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations. Deliberate abuse of formulations containing cellulose, either by inhalation or by injection, has resulted in the formation of cellulose granulomas.
Microcrystalline Cellulose is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Microcrystalline Cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is a mixture of two materials both of which are generally regarded as nontoxic: Microcrystalline Cellulose GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalations; oral capsules, powders, suspensions, syrups, and tablets; topical and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Carboxymethylcellulose sodium GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; intra-articular, intrabursal, intradermal, intralesional, and intrasynovial injections; oral drops, solutions, suspensions, syrups and tablets; topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Nonmedicinal Ingredients.